Introduction
Let’s face it, there are a a lot of different Arduino boards out there. How do you decide which one you need for your project? In this tutorial, we’ll take a look at the diverse world of Arduino boards. We’ll begin with a tabular overview of the features each board has. Then we’ll delve deeper into each board, examining the pros, cons, and example use-cases.
Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It’s intended for artists, designers, hobbyists, and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments. Or more simply, you load on some code and it can read sensors, perform actions based on inputs from buttons, control motors, and accept shields to further expand it’s capabilities. Really, you can do almost anything.
All Arduino boards have one thing in common: they are programmed through the Arduino IDE. This is the software that allows you to write and upload code. Beyond that, there can be a lot of differences. The number of inputs and outputs (how many sensors, LEDs, and buttons you can use on a single board), speed, operating voltage, and form factor are just a few of the variables. Some boards are designed to be embedded and have no programming interface (hardware) which you would need to buy separately. Some can run directly from a 3.7V battery, others need at least 5V. Check the chart on the next page to find the right Arduino for your project.
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-learning-and-teaching/?&tag=Coding
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-learning-and-teaching/?&tag=makerspace



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

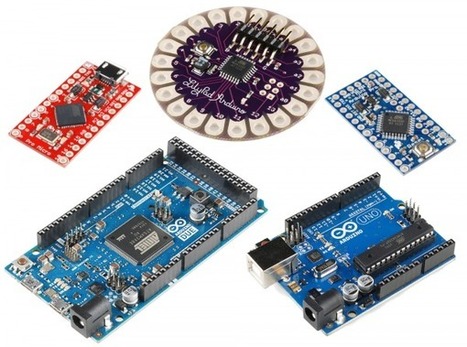








Introduction
Let’s face it, there are a a lot of different Arduino boards out there. How do you decide which one you need for your project? In this tutorial, we’ll take a look at the diverse world of Arduino boards. We’ll begin with a tabular overview of the features each board has. Then we’ll delve deeper into each board, examining the pros, cons, and example use-cases.
Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It’s intended for artists, designers, hobbyists, and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments. Or more simply, you load on some code and it can read sensors, perform actions based on inputs from buttons, control motors, and accept shields to further expand it’s capabilities. Really, you can do almost anything.
All Arduino boards have one thing in common: they are programmed through the Arduino IDE. This is the software that allows you to write and upload code. Beyond that, there can be a lot of differences. The number of inputs and outputs (how many sensors, LEDs, and buttons you can use on a single board), speed, operating voltage, and form factor are just a few of the variables. Some boards are designed to be embedded and have no programming interface (hardware) which you would need to buy separately. Some can run directly from a 3.7V battery, others need at least 5V. Check the chart on the next page to find the right Arduino for your project.
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-learning-and-teaching/?&tag=Coding
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-learning-and-teaching/?&tag=makerspace