Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
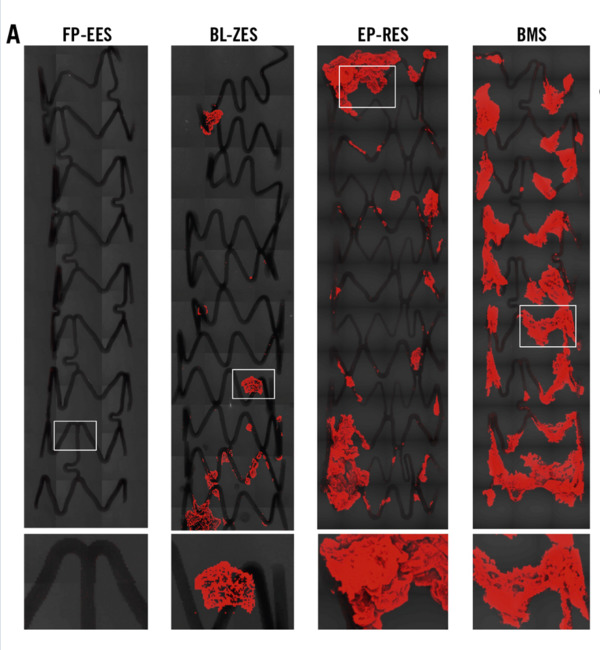
Overall, antithrombogenicity was better in the order FP-EES, BL-ZES, EP-RES and BMS. Although three durable polymer DES showed greater albumin coverage as compared to BMS, albumin intensity indicating concentration of albumin was not equivalent in three durable polymer DES. The results of albumin adsorption might be the cause of differences in platelet adhesion seen in the three different types of durable polymer DES and BMS, although other factors such as the adhesion of leukocytes also probably play a role. Because we also showed that the antiproliferative agents loaded onto DES have some thromboresistant properties, it is important to acknowledge the potential contribution of the antiproliferative agents as contributing to the thromboresistant effects seen in the different DES studied. These experiments may provide insight into the suitability of different durable polymer DES for shortening DAPT duration.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
The launch of Esprit BTK also compensates for the withdrawal of Absorb BVS, although the Esprit BTK market is currently not comparable to the coronary stent market at all. However, with a market volume of more than 200,000, it will be able to recoup the development costs of absorbable stents and support the development of a new generation of absorbable coronary stents. In February, CE approved Biotronik's next-generation resorbable coronary stent, Freesolve, and overseas response to Freesolve has been very favorable. This will also provide impetus for Abbott's absorbable coronary stent development. We are looking forward to the resurgence of absorbable stents in the future.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
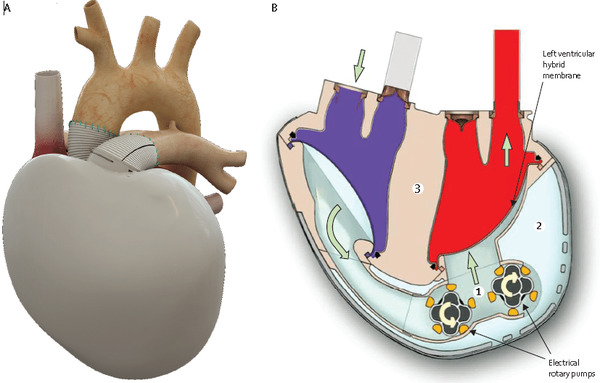
Carmat aims to meet a major public health challenge related to cardiovascular diseases, namely heart failure, the leading cause of death in the western world. More specifically, Carmat aims to provide a lasting solution for the treatment of terminal heart failure, a disease for which there are very few effective options today, the main one being heart transplants.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
In this study, patients with carotid artery plaque in which MNPs were detected had a higher risk of a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from any cause at 34 months of follow-up than those in whom MNPs were not detected.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
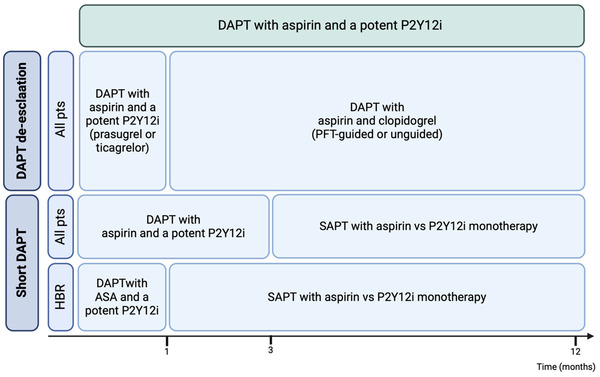
Antiplatelet therapy is a cornerstone in the management of acute coronary syndromes. Even if recent guidelines confirm the use of a dual antiplatelet regimen consisting of aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor as the standard of care, dramatic changes in stent technology and features of patients have led to greater attention to the balance between hemorrhagic and thrombotic risk. Taking into consideration all these aspects, recent years have been characterized by an effort to define alternative strategies to limit hemorrhagic complications while ensuring an efficacious antithrombotic effect, which have been tested in numerous RCTs, such as P2Y12 monotherapy and guided or unguided downgrading of DAPT. Evidence regarding the net clinical benefit of these alternative strategies in patients with high bleeding risk has led to an update of the latest guidelines.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy following 3-month dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is not inferior to 12-month DAPT regarding net adverse clinical events in patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents, according to study findings published in the Journal of the American Medical Association Network Open.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
This retrospective single-center registry study included all consecutive patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for a de novo left main coronary artery lesion using drug coated-balloon (DCB)-only strategy between August 2011 and December 2018. To best of our knowledge, no previous studies of DCB-only strategy of treating de novo left main coronary artery disease, exist. The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) including cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and target lesion revascularization (TLR).

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Despite substantial advances in stent technology, ISR remains the primary cause of target lesion failure after PCI. The available evidence supports the use of DCB angioplasty and DES implantation as first-line therapies for ISR. Nonetheless, the choice between DES and DCB should be individualized based on clinical, anatomical, and technical factors. In this regard, intravascular imaging with IVUS and OCT can be useful for identifying the primary mechanisms leading to ISR and guiding the interventional strategy during PCI.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
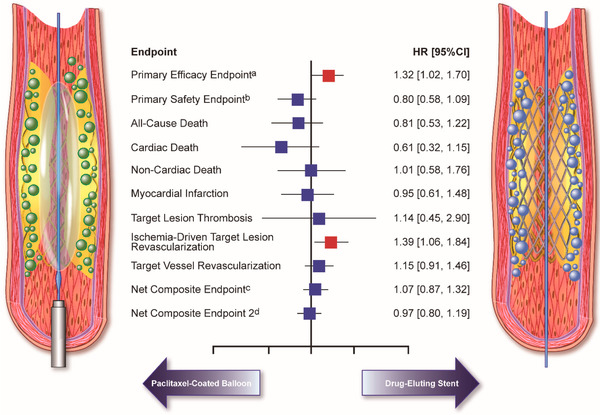
In the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment (HTA)-funded BASIL-3 randomised controlled trial (RCT), neither drug-coated balloon (DCB) angioplasty with or without bare metal stent nor drug-eluting stent (DES), when used in the femoropopliteal segment, conferred a hypothesised clinical benefit over femoropopliteal plain balloon angioplasty with or without bare metal stent.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
The current state of femoropopoliteal revascularization allows for an endovascular approach to address most PAD lesions, regardless of clinical syndrome, reserving surgery for special cases or refractory lesions. Innovation in devices has resulted in improved patency rates comparable to those of surgical revascularization, with the added benefit of rapid recovery time, including allowing for outpatient-based procedures. Newer technologies, including plaque modification devices, DCBs, and intravascular imaging, have resulting in greater preservation of the native vessel without the need for stent implantation. These developments, combined with a general philosophy of “leave the least behind” with regards to stenting, have shown significant improvement in procedural technical success rates and freedom from TLR.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
With IN.PACT AV Access having demonstrated superior outcomes at three years with the IN.PACT AV DCB versus plain balloon angioplasty for dialysis access—as per a presentation from Holden at last year’s CX Symposium—the speaker initially noted that it is currently the only randomised pivotal study to have produced “consistent and sustained clinical benefit” with an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) treatment device at such a long-term follow-up.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Avantage majeur rapporté et faisant tout l’intérêt de ce stent: la motricité vasculaire est restaurée à 12 mois et se révèle supérieure à celle observée avec le stent classique, grâce à la résorption du biopolymère faisant la liaison entre les structures métalliques du dispositif qui se retrouvent alors indépendantes les unes des autres, apportant ainsi de la souplesse au stent.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
HF hospitalization rates and symptom burdens remain high in patients with HF. In addition to drug therapy, several interventional procedures for neuromodulation have been increasingly investigated in patients with HF. This article summarizes the pathophysiologic rationale and latest clinical evidence for interventional neuromodulating therapies investigated in HF, including catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation (RDN), unilateral electrical baroreflex activation therapy (BAT), and endovascular BAT

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Autonomic modulation has been proposed as a potential therapeutic strategy aimed at reduction of systemic inflammation. Such therapies, complementary to drug and device-based therapies may lead to improved patient outcomes and reduce disease burden. Most professional societies currently do not provide a clear recommendation on the use of neuromodulation techniques in HF. These include direct and indirect vagal nerve stimulation, spinal cord stimulation, baroreflex activation therapy, carotid sinus stimulation, aortic arch stimulation, splanchnic nerve modulation, cardiopulmonary nerve stimulation, and renal sympathetic nerve denervation. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of neuromodulation in HF.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
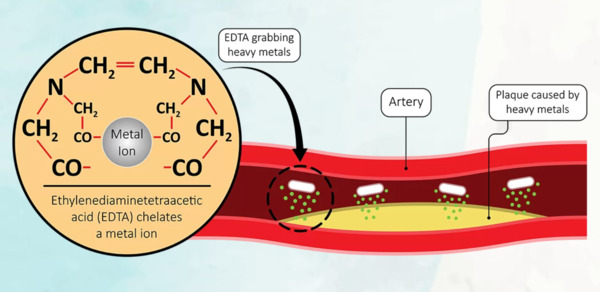
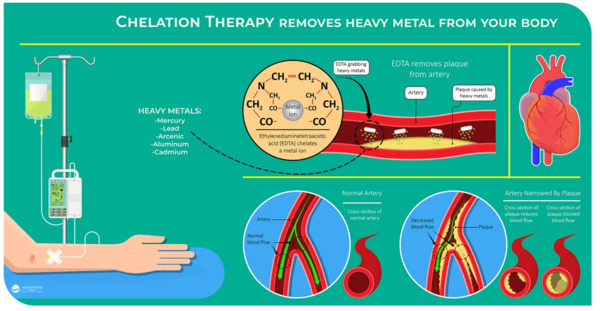
EDTA-3Na/H2O or EDTA-2Na/H2O with longer circulation times resulted in greater calcium reduction in atherosclerotic lesion. EDTA may have a potential therapeutic option for the treatment of atherosclerotic calcified lesions.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Chelation therapy works by administering chelating agents that bind to heavy metals and safely remove them from the body through the urine. These compounds work by forming multiple chemical bonds to a metal ion.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
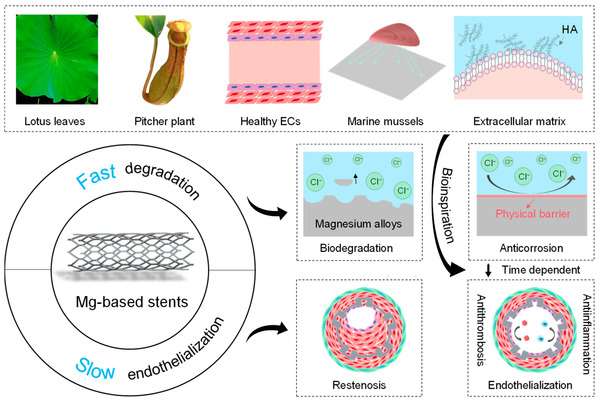
The investigation underscores the significance of corrosion resistance and biocompatibility in diverse anatomical cavities. The quintessential biodegradable Mg stent ought to possess stellar mechanical properties, biodegradability, and commendable biocompatibility while taking into account site-specific requisites. The utilization of degradable stents obviates the necessity for secondary interventions and proffers unparalleled advantages in disparate luminal environments. Mg alloys have garnered attention as exceedingly promising materials for multifaceted human implants, owing to their mechanical attributes and degradation kinetics. Nevertheless, challenges such as mechanical support duration, degradation kinetics, biological functionality, and compatibility with minimally invasive therapeutic modalities necessitate redressal for prospective device translation.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
The disadvantages of Mg-based stents include their rapid degradation and insufficient endothelialization after implantation. Bioinspired strategies for Mg-based stents can increase not just the corrosion resistance but also their biocompatibility. For instance, bioinspired strategies would exhibit slow degradation by constructing a bioinspired physical barrier to prevent exposure of Mg-based stents to the ambient atmosphere and achieve fast endothelialization after implantation to tackle restenosis problems.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
These findings suggest that low LDL-C levels are associated with an increased bleeding risk within 3 months among patients with minor ischemic stroke or high-risk transient ischemic attack who are receiving dual antiplatelet therapy, especially those taking ticagrelor-aspirin.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
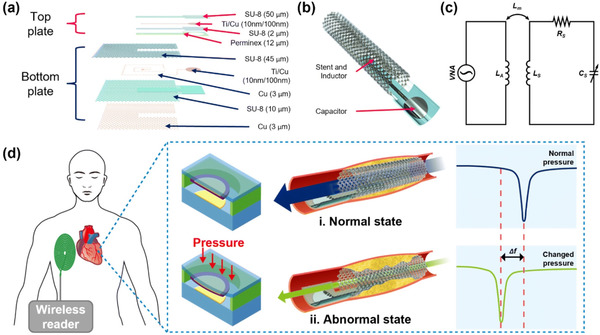
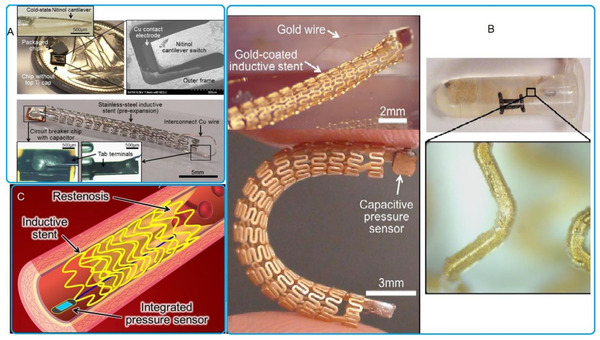
The preliminary findings confirmed the proposed smart stent's higher level of structural integrity, durability and repeatability. Finally, the practical feasibility of the smart stent is demonstrated by monitoring diastole and systole at various beat rates using a phantom. The results of the phantom study showed a similar pattern to the human model, indicating the potential use of the proposed multifunctional smart stent for real-time applications.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
The stent may be used as an antenna coil and may replace supplemental circular or planar coils for receiving power. The stent shape and dimensions may be modified to allow them to receive energy and also provide longer life, thereby having a longer-term treatment. This study is expected to introduce a key database of associated works for researchers in the field. Lastly, the problems and challenges involved in improving the devices and long-term treatments were discussed in detail.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
In this paper, we present a stent antenna for intravascular monitoring and implantable wireless applications that employ the entire stent as an antenna. The main contribution of this work was the manipulation of the current distributions of the stent for good radiation performance with a short stent length by exploiting a single connector between each unit of the stent. Unlike a general stent, wherein each unit is connected with multiple connectors, our proposed stent can achieve good EM radiation, maintain good mechanical strength, and remain within fracture limits during balloon expansions. A prototype was designed, fabricated, and experimentally examined with an EM anechoic chamber. The fabricated stent antenna demonstrated an omnidirectional radiation pattern, a gain of 1.38 dBi, and a radiation efficiency of 74.5% at the resonant frequency of 2.07 GHz. The results of this research should contribute to the development of implantable wireless communications and intravascular monitoring of cardiovascular diseases.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
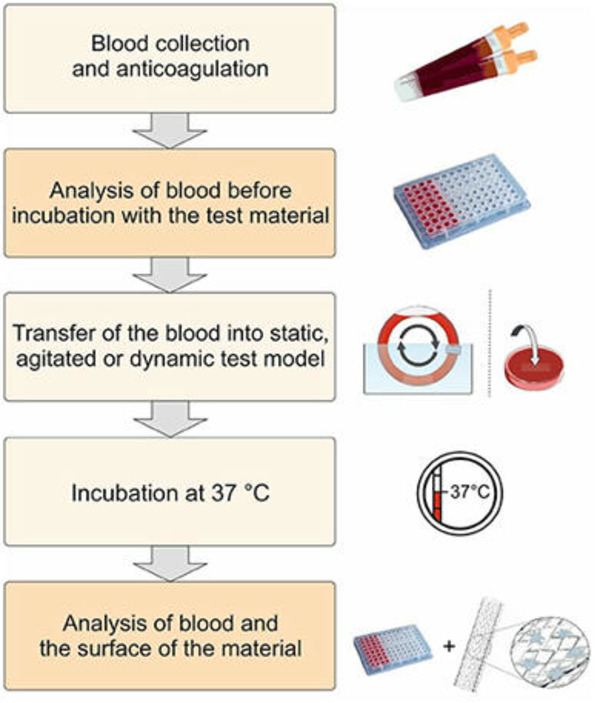
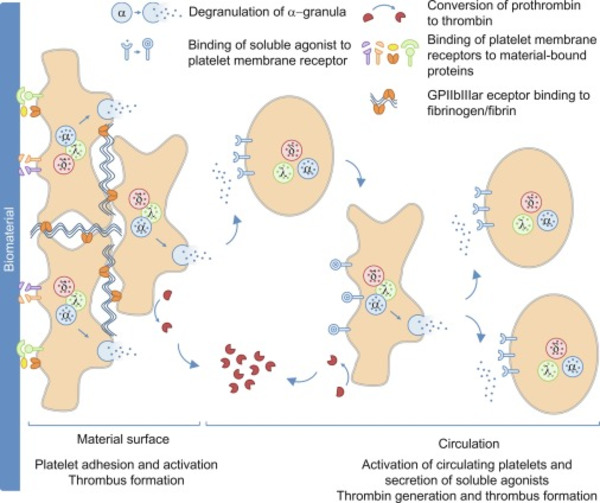
The interaction of biomaterials with blood leads to cellular as well as humoral reactions, which can result in an unwanted inflammation and activation of coagulation and/or fibrinolysis. Thus, the development of biomaterials with an improved hemocompatibility increases the tolerability and minimizes unwanted side effects, such as thrombus formation. Therefore, during the development of new blood-contacting medical devices, not only the mechanical and chemical characteristics should play an important role, but also the hemocompatibility. Furthermore, to prove the safety and reliability of new products, hemocompatibility analyses should include appropriate references and follow the ISO 10993-4 standard.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
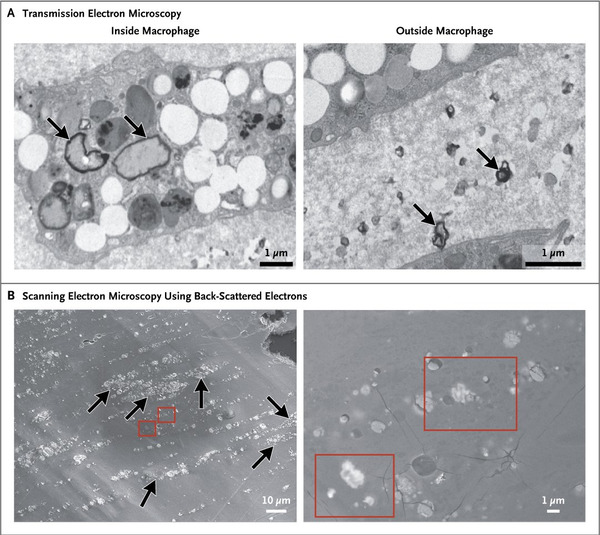
There is currently no standardized test method for in vitro dynamic thrombogenicity assessment of medical devices and biomaterials. This tool will effectively enable users to differentiate device materials with different thrombogenic potentials against standard negative and positive control materials and a marketed comparator device with known thrombogenicity profile.

|
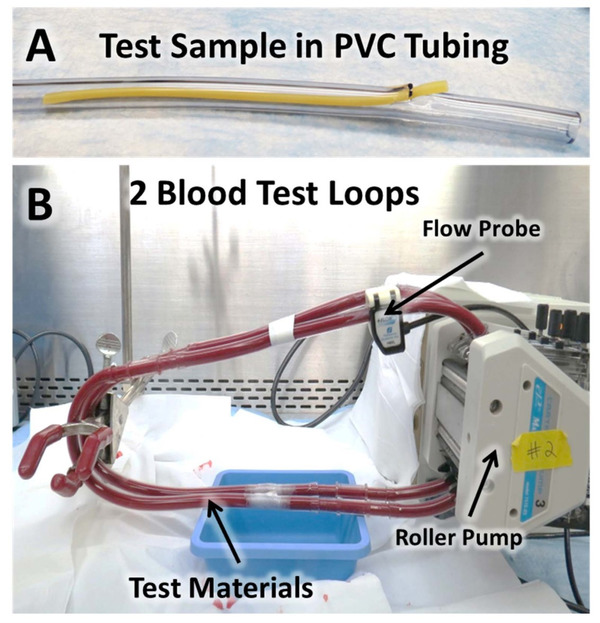
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
These results demonstrated that multiple animal blood sources (particularly donor ovine and bovine blood) may be suitable alternatives to fresh human blood for dynamic thrombogenicity testing when appropriate control materials and donor-specific anticoagulation levels are used.
|

Curated by Beeyond
BEEYOND is a consulting company in the field of disruptive innovation, accompanying established companies on out-of-the-core growth strategy, from creation of new concepts to product launch. Reach us at: contact@beeyond.fr.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...