Learning doesn't have to be a "loner" experience.
Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky suggested that knowledge is constructed through our interactions with others.
MOOCs (Massive Open Online Learning) leverage our inherent social needs by bringing people together to learn the same material in a virtual group. Students can express what they're feeling and experiencing with others in a shared space, making the learning journey more enjoyable and less daunting.
As people gain confidence, they often enjoy friendly competition with fellow learners to push themselves to compete exercises and assignments. Recognition is part of our need for building self-esteem—and some courses have gamification built in to reward student accomplishments and community helpfulness.
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-learning-and-teaching/?tag=Social+Learning
Via Gust MEES



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

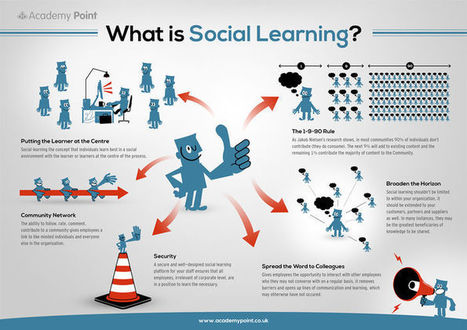

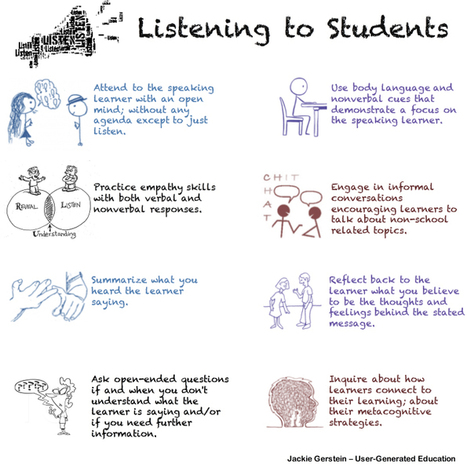







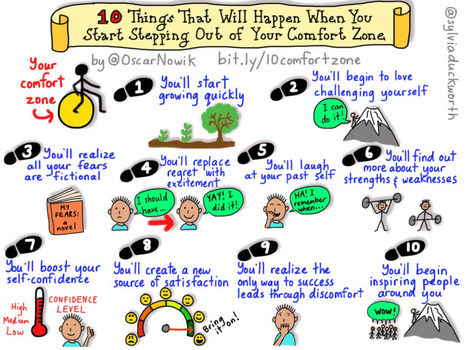









Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky suggested that knowledge is constructed through our interactions with others.
MOOCs (Massive Open Online Learning) leverage our inherent social needs by bringing people together to learn the same material in a virtual group. Students can express what they're feeling and experiencing with others in a shared space, making the learning journey more enjoyable and less daunting.
As people gain confidence, they often enjoy friendly competition with fellow learners to push themselves to compete exercises and assignments. Recognition is part of our need for building self-esteem—and some courses have gamification built in to reward student accomplishments and community helpfulness.
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://www.scoop.it/t/21st-century-learning-and-teaching/?tag=Social+Learning
This is an interesting intro to social constructionism as it applies to eLearning. I hope the MOOCs do what they suggest and are not just an attempt to throw jargon out there.