Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|




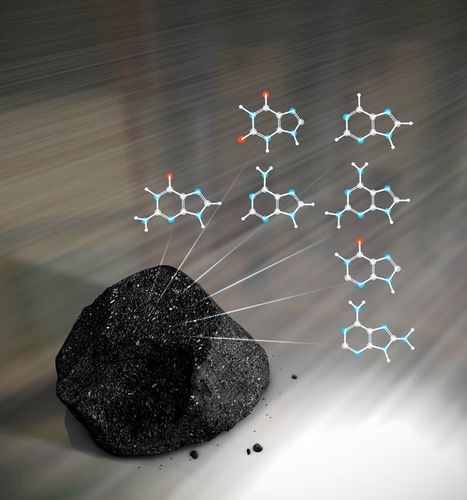











The lack of pyrimidine diversity in meteorites remains a mystery since prebiotic chemical models and laboratory experiments have predicted that these compounds can also be produced from chemical precursors found in meteorites. Here the authors report the detection of nucleobases in three carbonaceous meteorites using state-of-the-art analytical techniques optimized for small-scale quantification of nucleobases down to the range of parts per trillion (ppt). In addition to previously detected purine nucleobases in meteorites such as guanine and adenine, they identify various pyrimidine nucleobases such as cytosine, uracil, and thymine, and their structural isomers such as isocytosine, imidazole-4-carboxylic acid, and 6-methyluracil, respectively. Given the similarity in the molecular distribution of pyrimidines in meteorites and those in photon-processed interstellar ice analogues, some of these derivatives could have been generated by photochemical reactions prevailing in the interstellar medium and later incorporated into asteroids during solar system formation. This study demonstrates that a diversity of meteoritic nucleobases could serve as building blocks of DNA and RNA on the early Earth. All DNA/RNA nucleobases were identified in carbonaceous meteorites. Having been provided to the early Earth as a component in carbonaceous meteorites, these molecules might have played a role for the emergence of genetic functions in early life.