Targeting two brain tumor-associated proteins-;rather than one-;with CAR T cell therapy shows promise as a strategy for reducing solid tumor growth in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM), an aggressive form of brain cancer, according to early results from the first six patients treated in an ongoing Phase I clinical trial led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine's Abramson Cancer Center.
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
Pierre-Luc Jellimann 's curator insight,
October 23, 2022 10:52 AM
Etude intéressante sur l'efficacité des CAR-T cells et surtout des TCR-T cells dans le traitement des tumeurs solides (mélanomes++) |
|




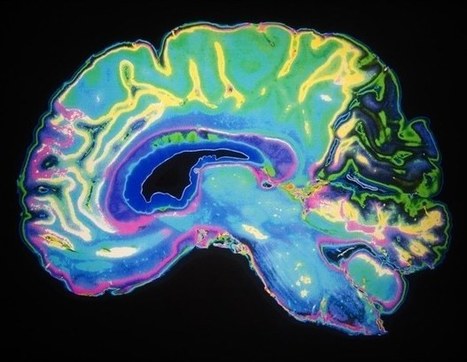









Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive type of cancerous brain tumor in adults. People with GBM generally expect to live 12 to 18 months after diagnosis. Despite decades of research, there is no known cure for GBM, and treatments have only a limited effect on extending an individual's life expectancy. However, researchers have tested a technology that delivers CAR-T cells targeting two proteins commonly found in brain tumors: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), estimated to be present in 60% of all GBMs, and interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 (IL13Rα2), which is expressed in over 75% of GBMs. While CAR-T cell therapy for blood cancers is usually administered intravenously, the researchers administered these dual-targeted CAR-T cells intrathecally, by injection into the cerebrospinal fluid, so that the modified cells could reach the tumors more directly in the brain. Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans taken 24 to 48 hours after administration of dual-targeted CAR-T cells targeting EGFR and IL13Rα2 revealed a reduction in tumor size in all six patients, and these reductions were maintained up to several months later in a subgroup of patients.