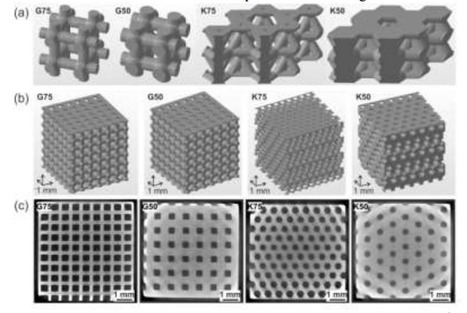
In ‘Application of high resolution DLP stereolithography for fabrication of tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone regeneration,’ researchers examine how to make complex, stable scaffolds based on β-tricalcium. Typically, there are obstacles to finding materials and techniques suitable for creating structures capable of sustaining cell life.
The authors are aware of the necessities in tissue engineering: the material cannot be toxic, obviously, as that would cause further health issues in a patient, biodegradability is key, with the material being absorbed along with suitable bone growth, and porosity and density must be suitable too, balanced out with proper strength.
DLP 3D printing has proven successful for creating scaffolds due to comprehensive irradiation over the whole cross-section, and shorter processing times in comparison to other processes. The researchers focused on DLP 3D printing for this study, in relation to the use of calcium phosphate structures that are not only complex and high resolution but also strong. The team assessed both rectilinear grid structure and hexagonal geometries (at 50 and 75 percent porosity) for mechanical properties, with complete chemical analyses performed before and after bioprinting.
Via Dr. Stefan Gruenwald



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...