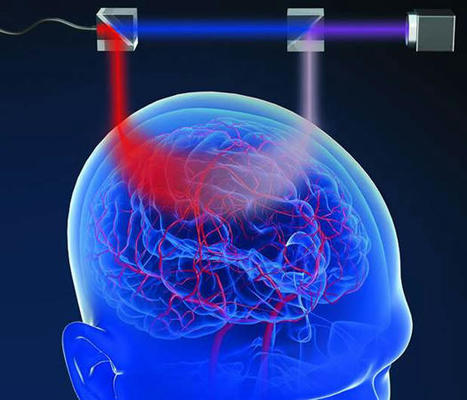
A new, noninvasive method for measuring brain blood flow with light has been developed by biomedical engineers and neurologists at the University of California, Davis, and used to detect brain activation.
The new method, functional interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy, or fiDWS, promises to be cheaper than existing technology and could be used for assessing brain injuries, or in neuroscience research.
The human brain makes up 2% of our body weight but takes 15% to 20% of blood flow from the heart. Measuring cerebral blood flow is important for diagnosing strokes, and for predicting secondary damage in subarachnoid hemorrhages or traumatic brain injuries. Doctors who provide neurological intensive care, would also like to monitor a patient's recovery by imaging brain blood flow and oxygenation.
Existing technology is expensive and cannot be applied continuously or at the bedside. For example, current techniques to image cerebral blood flow require expensive MRI or computed tomography scanners. There are light-based technologies, such as near-infrared spectroscopy, but these also have drawbacks in accuracy.
The new method takes advantage of the fact that near-infrared light can penetrate through body tissues. If you shine a near-infrared laser on someone's forehead, the light will be scattered many times by tissue, including blood cells. By picking up the fluctuation signal of the light that finds its way back out of the skull and scalp, you can get information about blood flow inside the brain.
read more at https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-05-brain-blood.html



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...