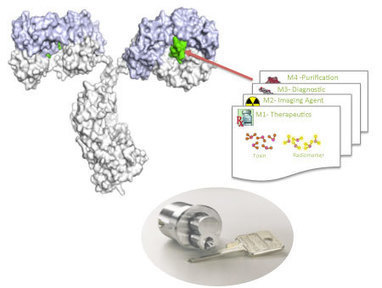
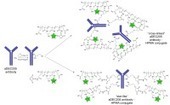
AbstractThe convergence of advanced understanding of biology with chemistry has led to a resurgence in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), especially with two recent product approvals. Design and development of ADCs requires the synergistic combination of the monoclonal antibody, the linker and the payload. Advances in antibody science has enabled identification and generation of high affinity, highly selective, humanized or human antibodies for a given target. Novel linker technologies have been synthesized and highly potent cytotoxic drug payloads have been created. As the first generation of ADCs utilizing lysine and cysteine chemistries moves through the clinic and into commercialization, second generation ADCs involving site specific conjugation technologies are being evaluated and tested. The latter aim to be better characterized and controlled, with wider therapeutic indices as well as improved pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) profiles. ADCs offer some interesting physicochemical properties, due to conjugation itself, and to the (often) hydrophobic payloads that must be considered during their CMC development. New analytical methodologies are required for the ADCs, supplementing those used for the antibody itself. Regulatory filings will be a combination of small molecule and biologics. The regulators have put forth some broad principles but this landscape is still evolving.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...