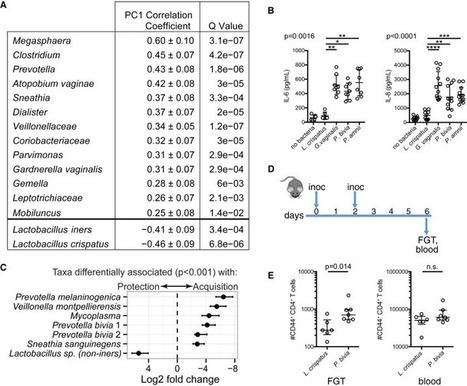
The potential impact of cervicovaginal bacteria on HIV susceptibility is not well-defined.
Gosmann et al. (2017) identify anaerobic cervicovaginal bacterial communities and
specific taxa highly prevalent in young healthy South African women that increase
their HIV risk. These findings might be leveraged to reduce HIV acquisition in women.
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|