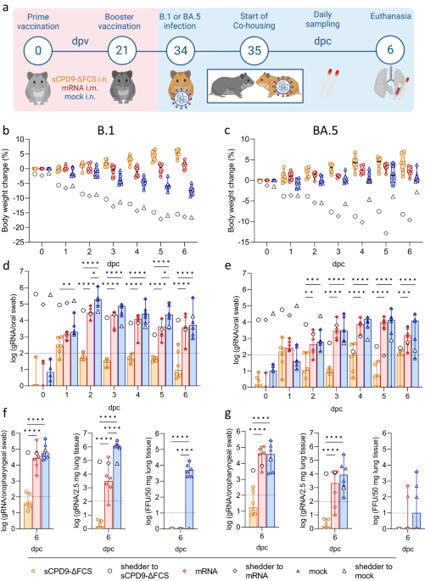
The development of effective SARS-CoV-2 vaccines has been essential to control COVID-19, but significant challenges remain. One problem is intramuscular administration, which does not induce robust mucosal immune responses in the upper airways—the primary site of infection and virus shedding. Here we compare the efficacy of a mucosal, replication-competent yet fully attenuated virus vaccine, sCPD9-ΔFCS, and the monovalent mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 in preventing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1 and Omicron BA.5 in two scenarios. Firstly, we assessed the protective efficacy of the vaccines by exposing vaccinated male Syrian hamsters to infected counterparts. Secondly, we evaluated transmission of the challenge virus from vaccinated and subsequently challenged male hamsters to naïve contacts. Our findings demonstrate that the live-attenuated vaccine (LAV) sCPD9-ΔFCS significantly outperformed the mRNA vaccine in preventing virus transmission in both scenarios. Our results provide evidence for the advantages of locally administered LAVs over intramuscularly administered mRNA vaccines in preventing infection and reducing virus transmission. In this study, the authors evaluated the protective capacity of a mucosal, live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and show that it induces systemic and mucosal humoral immunity, protects from clinical disease symptoms, and prevents virus transmission in hamsters more efficiently than an intramuscular mRNA vaccine.
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|