Abstract
Objectives To evaluate safety and efficacy of weekly (qw) and every other week (q2w) dosing of sarilumab, a fully human anti-interleukin 6 receptor α (anti-IL-6Rα) monoclonal antibody, for moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods In this dose-ranging study, patients (n=306) with active RA, despite methotrexate, were randomly assigned to placebo or one of five subcutaneous doses/regimens of sarilumab: 100 mg q2w, 150 mg q2w, 100 mg qw, 200 mg q2w, 150 mg qw for 12 weeks, plus methotrexate. The primary end point was ACR20 at Week 12. Secondary endpoints included ACR50, ACR70, Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (C reactive protein). Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and efficacy in population subgroups were assessed.
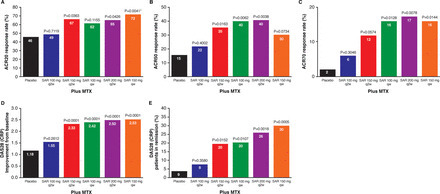
Results The proportion of patients achieving an ACR20 response compared with placebo was significantly higher for sarilumab 150 mg qw (72.0% vs 46.2%, multiplicity adjusted p=0.0203). Higher ACR20 responses were also attained with 150 mg q2w (67%; unadjusted (nominal) p=0.0363) and 200 mg q2w (65%; unadjusted p=0.0426) versus placebo. Sarilumab ≥150 mg q2w reduced C reactive protein, which did not return to baseline between dosing intervals. Infections were the most common adverse event; none were serious. Changes in laboratory values (neutropenia, transaminases and lipids) were consistent with reports with other IL-6Rα inhibitors.
Conclusions Sarilumab improved signs and symptoms of RA over 12 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe RA with a safety profile similar to reports with other IL-6 inhibitors. Sarilumab 150 mg and sarilumab 200 mg q2w had the most favourable efficacy, safety and dosing convenience and are being further evaluated in Phase III.
Via
Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...