I feel so alive.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account

 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
Know all about the Human Genome Project and its significance for health and other areas.
THE OFFICIAL ANDREASCY's insight:
Decoding the Human Genome Project: the basics and its potential benefits. 
Andreas Christodoulou's curator insight,
August 8, 2016 10:07 AM
Revealing the secrets of the Human Genome: http://tinyurl.com/DecodingHumanGenomeProject The basics and its potential benefits for health and other areas. 
Stephania Savva, Ph.D's curator insight,
August 8, 2016 10:07 AM
One of the most important research endeavors of the millennium. Know more about the Human Genome Project.
There's a lot of exciting developments happening in the world of technology - don't fall behind. Sign up so we can keep in touch.
THE OFFICIAL ANDREASCY's insight:
The newsletter will boil it all down for you, providing only the most relevant information and sending it straight to your inbox. We also offer insightful tips, tricks and time-saving techniques with fresh and useful resources.
Click here to sign up for it. See you on the inside! ;) 
Jane Shamcey's curator insight,
June 8, 2015 7:12 AM
The best way to keep on top of the latest tech information is to subscribe to our newsletter: http://swyy.co/EAqLdtE 
Stephania Savva, Ph.D's curator insight,
June 8, 2015 7:14 AM
Seek no further for reliable and up to date tech news from around the globe delivered right to your inbox. Also check their latest tweets: https://twitter.com/andreaschriscy
From
www
The chemistry of life is built on left-handed and right-handed molecules that can have completely different functions. These so-called enantiomers of a chiral compound can now be reliably distinguished via microwaves. The new method can in principle even detect these enantiomers in mixtures of substances. The procedure also holds promise for the development of a technique to separate left- from right-handed variants of a molecule, reports the international research team, which also includes Melanie Schnell of the Center for Free Electron Laser Science CFEL. CFEL is a joint venture of DESY, the Max Planck Society and the University of Hamburg.
Many chemical compounds exist in two variants, called enantiomers. These consist of the same elements but act as mirror images of each other. In reference to our hands, which are also mirror images, such molecules are called chiral, after the ancient Greek word for hand, cheiros. "Distinguishing the two variants of a chiral compound is one of the most difficult, yet most important tasks in analytical chemistry," says David Patterson from the University of Harvard, who is the first author of the "Nature" paper. In biology, but also in many chemical reactions, the chirality of a molecule plays an important role. The chemistry of life, for instance, builds almost exclusively on left-handed amino acids and right-handed sugar molecules. Why and how nature does this, is a largely unanswered question.
Chemical syntheses often produce both variants (enantiomers) of a compound in equal amounts. "The 'wrong' sort of a compound can function completely differently in an organism," explains Melanie Schnell, who leads an independent Max Planck Research Group for Structure and Dynamics of Molecules at CFEL. "In the best case it is just ineffective. In the worst case it is toxic." Especially the pharmaceutical industry is hugely interested in the production of pure enantiomers, and the development and improvement of methods to synthesise or later enrich a certain enantiomer of some active substances is an active and broad field of research.
The researchers tested their method using the organic compound 1,2-propanediol, which can be bought as pure enantiomers. The technique could not only reliably differentiate between the two variants, but also tell the mixing ratio of a mixture of enantiomers. The microwave frequency can be extremely fine tuned to the desired rotational state of a molecule. This way, the technique can also probe mixtures of substances. "We can soon measure mixtures of different compounds and determine the enantiomer ratios of each," explains Schnell. In a next step the researchers plan to apply the technique in a broadband spectrometer at CFEL that could then measure the enantiomer ratios in mixtures of substances.
"In the longer run, the method opens the exciting perspective to develop a technique for separating enantiomers," explains Doyle. To this end, one enantiomer could be excited with a laser. Then, another laser that acts differently on excited molecules than on not excited molecules can be used to separate both enantiomers. These laser pulses could be repeatedly applied to a room-temperature vapour in a closed cell. Typically, only one in ten thousand molecules would be in the desired rotational state at any moment, but a significant enantiomeric excess could be rapidly accumulated.
Via Dr. Stefan Gruenwald |
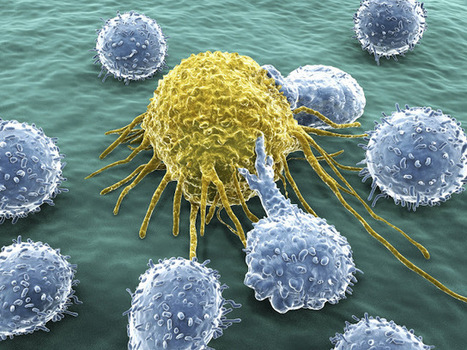
Stay updated on the latest types of cancer treatments. Find out what you need to know!
THE OFFICIAL ANDREASCY's insight:
How cancer is treated! 
Andreas Christodoulou's curator insight,
October 18, 2016 4:53 AM
What's new in cancer research and treatment: http://tiny.cc/LatestCancerTreatments
Some of the latest news on our site. Keep reading!
- What's New Series
THE OFFICIAL ANDREASCY's insight:
We think you'll enjoy this. More to come... 
Andreas Christodoulou's curator insight,
April 20, 2016 6:51 AM
Go ahead watch this video. Be sure to read our articles for more information.
From
phys
A team of researchers working at China's University of Science and Technology has succeeded in developing a chemical mapping technique capable of revealing the constituent atoms of a single molecule.
Visualizing individual molecules with chemical recognition is a longstanding target in catalysis, molecular nanotechnology and biotechnology. Molecular vibrations provide a valuable 'fingerprint' for such identification. Vibrational spectroscopy based on tip-enhanced Raman scattering allows us to access the spectral signals of molecular species very efficiently via the strong localized plasmonic fields produced at the tip apex. However, the best spatial resolution of the tip-enhanced Raman scattering imaging is still limited to 3−15 nanometres, which is not adequate for resolving a single molecule chemically. Here we demonstrate Raman spectral imaging with spatial resolution below one nanometre, resolving the inner structure and surface configuration of a single molecule. This is achieved by spectrally matching the resonance of the nanocavity plasmon to the molecular vibronic transitions, particularly the downward transition responsible for the emission of Raman photons. This matching is made possible by the extremely precise tuning capability provided by scanning tunnelling microscopy. Experimental evidence suggests that the highly confined and broadband nature of the nanocavity plasmon field in the tunnelling gap is essential for ultrahigh-resolution imaging through the generation of an efficient double-resonance enhancement for both Raman excitation and Raman emission. Our technique not only allows for chemical imaging at the single-molecule level, but also offers a new way to study the optical processes and photochemistry of a single molecule. Via Dr. Stefan Gruenwald
THE OFFICIAL ANDREASCY, Your Daily Rendezvous With the Latest Tech & Science news. Get the awesome and free news straight to your inbox!

Wilfried Andral's curator insight,
September 13, 2014 3:54 AM
The Best Tech site around! Check it out! 
Jane Shamcey's curator insight,
September 13, 2014 3:56 AM
You should check it out!!!
Tech Blog: http://goo.gl/1mqMQk |