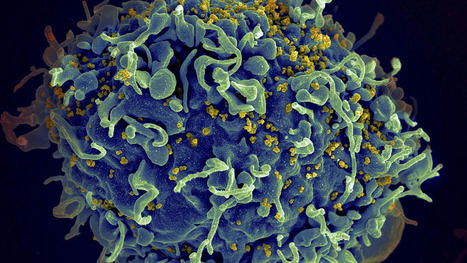
There is a “window of opportunity” in the weeks after someone is infected with HIV where treatment may lead to better control later on, researchers say. Treatment for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) four weeks after infection may make it possible to control the virus without medication in the long term, a new study has shown. The finding reinforces the importance of detecting HIV early, according to researchers from the French Institut Pasteur, CEA, Inserm, University of Paris Cité, and the University of Paris-Saclay. Treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy (ART) and can be taken as a pill or an injection. The goal is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level so the person has no risk of transmitting HIV.
This therapy is now so effective that it can fully control the virus, with researchers even exploring ways to cure it. This latest study looked at the impact of early treatment on primates with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), which is closely related to HIV. The researchers found that very early treatment for two years led to controlling the virus even after treatment was interrupted. “We show an association between early treatment and control of the infection after treatment is stopped, and our study indicates the existence of a window of opportunity to promote remission of HIV infection,” Asier Sáez-Cirión, head of the Institut Pasteur’s viral reservoirs and immune control unit and co-senior author of the study, said in a statement. A previous 2013 study in humans had shown a similar possibility, suggesting that early treatment could allow people to stop treatment, with the virus in a “state of remission”. The latest study also showed that the benefits of early treatment were lost if therapy was started just five months later. The findings were published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...







Amazing
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product-category/dmt/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/5-meo-dmt/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/4-aco-dmt/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/ayahuasca/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/changa-dmt/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-dmt-vape-pen/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/lsd-tabs/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-mimosa-hostilis-root-bark-powdered-mhrb/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/nn-dmt/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/amanita-muscaria/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-dragons-dynamite-truffles/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/golden-teachers/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-high-hawaiians-truffles/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/liberty-caps/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-microdosing-psilocybin-truffles-10-pack/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-microdosing-psilocybin-truffles-2-pack-in-stock/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-microdosing-psilocybin-truffles-20-pack/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/golden-teachers/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/buy-penis-envy-mushroom/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/codeine-promethazine/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/ecstasy-mdma/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/microdosing-psilocybin-truffles-1-pack-for-sale/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/mush-rocks-truffles-for-sale/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/pcp-powder/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/cocaine/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/methamphetamine/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/xanax/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/lsd-gel-tabs/
https://buypsychedelicdrugs.com/product/lsd-liquid/
https://caluaniemuelearoxidizeusa.com/product/buy-10l-caluanie-muelear-pasteurize/
https://caluaniemuelearoxidizeusa.com/product/buy-20l-caluanie-muelear-oxidize/
https://caluaniemuelearoxidizeusa.com/product/buy-5l-caluanie-muelear-pasteurize/
https://caluaniemuelearoxidizeusa.com/product/buy-caluanie-muelear-pasteurize/