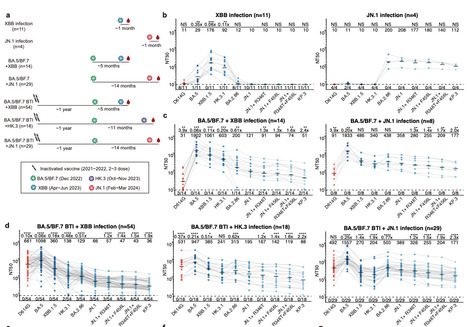
The ongoing evolution of SARS-CoV-2 continues to challenge the global immune barrier established by infections and vaccine boosters. Recently, the emergence and dominance of the JN.1 lineage over XBB variants have prompted a reevaluation of current vaccine strategies. Despite the demonstrated effectiveness of XBB-based vaccines against JN.1, concerns persist regarding the durability of neutralizing antibody (NAb) responses against evolving JN.1 subvariants. In this study, we compared the humoral immunogenicity of XBB and JN.1 lineage infections in human subjects with diverse immune histories to understand the antigenic and immunogenic distinctions between these variants. Similar to observations in naive mice, priming with XBB and JN.1 in humans without prior SARS-CoV-2 exposure results in distinct NAb responses, exhibiting minimal cross-reactivity.
Importantly, breakthrough infections (BTI) with the JN.1 lineage induce 5.9-fold higher neutralization titers against JN.1 compared to those induced by XBB BTI. We also observed notable immune evasion of recently emerged JN.1 sublineages, including JN.1+R346T+F456L, with KP.3 showing the most pronounced decrease in neutralization titers by both XBB and JN.1 BTI sera. These results underscore the challenge posed by the continuously evolving SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 and support the consideration of switching the focus of future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine updates to the JN.1 lineage.
Preprint in bioRxiv (April 22, 2024):
https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.19.590276



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...