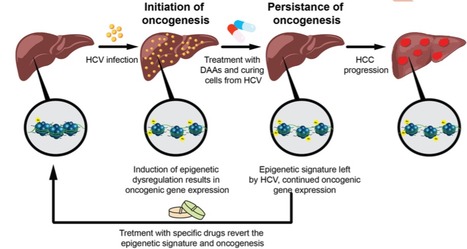
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in western countries. While direct acting antivirals (DAAs) therapy for HCV efficiently eradicates the infection, sustained virological response (SVR) following anti-HCV treatment does not eliminate the risk for HCC development. These HCV-induced epigenetic changes reprogram host gene expression and persist as an "epigenetic signature" following virus eradication. Treatment of HCV-cured cells with specific inhibitors reverted the epigenetic signature. These results suggest a "hit and run" scenario that may explain why some chronic HCV infected patients do proceed to develop HCC after HCV eradication.
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
Virus World provides a daily blog of the latest news in the Virology field and the COVID-19 pandemic. News on new antiviral drugs, vaccines, diagnostic tests, viral outbreaks, novel viruses and milestone discoveries are curated by expert virologists. Highlighted news include trending and most cited scientific articles in these fields with links to the original publications. Stay up-to-date with the most exciting discoveries in the virus world and the last therapies for COVID-19 without spending hours browsing news and scientific publications. Additional comments by experts on the topics are available in Linkedin (https://www.linkedin.com/in/juanlama/detail/recent-activity/)
Curated by
Juan Lama
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|










https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008181