Alopecia areata is driven by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and is reversed by JAK ...
Nature.com
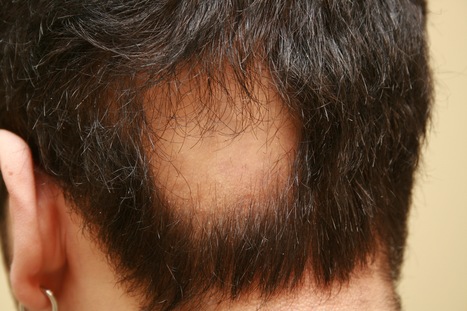
Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune disease resulting from damage of the hair follicle by T cells.

|
Scooped by Alfredo Corell |
Alfredo Corell's insight:
- Luzhou Xing,
- Zhenpeng Dai,
- Ali Jabbari,
- Jane E Cerise,
- Claire A Higgins,
- Weijuan Gong,
- Annemieke de Jong,
- Sivan Harel,
- Gina M DeStefano,
- Lisa Rothman,
- Pallavi Singh,
- Lynn Petukhova,
- Julian Mackay-Wiggan,
- Angela M Christiano
- & Raphael Clynes
- Affiliations
- Contributions
- Corresponding authors
- Nature Medicine (2014) doi:10.1038/nm.3645
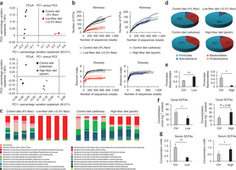
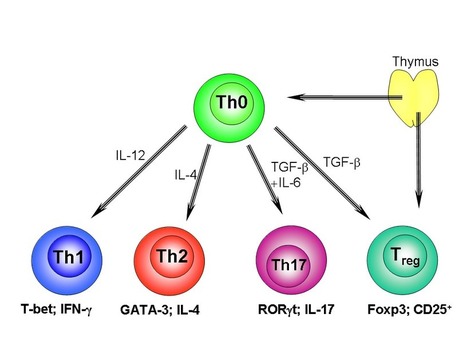
- Alopecia areata (AA) is a common autoimmune disease resulting from damage of the hair follicle by T cells. The immune pathways required for autoreactive T cell activation in AA are not defined limiting clinical development of rational targeted therapies1. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS)2 implicated ligands for the NKG2D receptor (product of the KLRK1 gene) in disease pathogenesis. Here, we show that cytotoxic CD8+NKG2D+ T cells are both necessary and sufficient for the induction of AA in mouse models of disease. Global transcriptional profiling of mouse and human AA skin revealed gene expression signatures indicative of cytotoxic T cell infiltration, an interferon-γ (IFN-γ) response and upregulation of several γ-chain (γc) cytokines known to promote the activation and survival of IFN-γ–producing CD8+NKG2D+ effector T cells. Therapeutically, antibody-mediated blockade of IFN-γ, interleukin-2 (IL-2) or interleukin-15 receptor β (IL-15Rβ) prevented disease development, reducing the accumulation of CD8+NKG2D+ T cells in the skin and the dermal IFN response in a mouse model of AA. Systemically administered pharmacological inhibitors of Janus kinase (JAK) family protein tyrosine kinases, downstream effectors of the IFN-γ and γc cytokine receptors, eliminated the IFN signature and prevented the development of AA, while topical administration promoted hair regrowth and reversed established disease. Notably, three patients treated with oral ruxolitinib, an inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2, achieved near-complete hair regrowth within 5 months of treatment, suggesting the potential clinical utility of JAK inhibition in human AA.
No comment yet.
Sign up to comment


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...