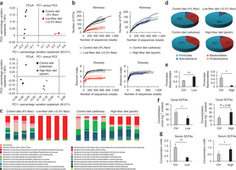
Dietary fibers are metabolized by the gut microbiota into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and have protective effects in inflammatory bowel disease. Here Benjamin J Marsland and colleagues report that mice fed a high-fiber diet have an altered microbiota and are protected from allergic airway inflammation. The SCFA propionate regulated allergic inflammation, bone marrow hematopoiesis and dendritic cell function. Taken together, these findings suggest that metabolites produced by the gut microbiota can influence hematopoiesis and immune responses in the lung.

|
Scooped by Alfredo Corell |

BrainImmune's comment,
February 11, 2014 3:20 PM
you are welcome
Sign up to comment


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...






Nature Medicine 20, 159–166 (2014) doi:10.1038/nm.3444